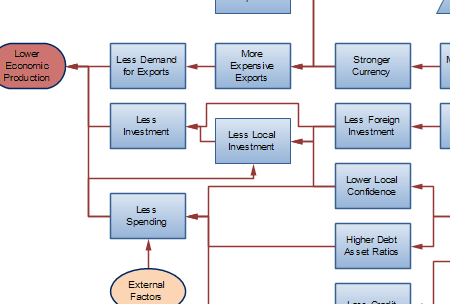
Factors contributing to Economic Growth and Causes for Recession and Economic Crisis
Do you also like to have a simple graphic overview of the factors contributing to economic growth and the causes for recession and economic crisis?
The daily economic news does not provide you with this overview. You hear statements about double-dips, a looming recession or even depression, huge growth and surplusses in China, a credit crisis, rising currencies, deleveraging of debts and more of this. Let’s have a look at the fundamental economic patterns behind all this.
The economy is complex. See attachment for the complete chart.
Nobel Prize in Economics winner Paul Krugman published in 1999 his book The Return of Depression Economics. In 2008, this book was republished with additional information on the crisis of 2008.
In his book Krugman explains why the economic and financial crisis of 2008 shouldn’t have come as a surprise and what we can learn from the crises of the last few decades in Latin America, Russia and Asia.
Throughout the book, Krugman shows the logical causes and effects in different economic situations. He explains the consequences of the economic decisions of various governments around the world in the face of financial crisis. We can strongly recommend to each who is interested in understanding the economy to read this book.
What we have done is to extract the economic principles that have been used in this book explaining the return of depression economics. We have sorted these principles under different headings. And we have created a simple graphic overview of how the economic factors in these principles are interacting and influencing each other.
This is a first in a series of publications on understanding how the economy works based on the lessons and material in Paul Krugman’s book. In this article we focus on the natural factors contributing to economic growth and causes for economic slowdown, recession and crisis.
Click on the picture in this article or download at the bottom of this page the high level overview that summarizes this graphically.
During the coming weeks, we will publish articles that focus on other aspects like the different economic actions that governments may take, currency regimes, economic bubbles and the vicious circle of economic crisis.
Possible Causes for Economic Slow-down and Recession
- Recessions are often caused by a lack in effective demand since people try to accumulate money (new savings are then possibly higher than investments).
- When people perceive that money is becoming scarce or may become scarce in the future, they will reduce spending and increase savings, lowering demand.
- When inflation in a country is higher than in other countries, the currency becomes more expensive, exports become more expensive and exports will decline or grow slower, lowering the economic growth.
- When financial bubbles burst and asset prices decline, investment and consumption decline and thus overall demand declines.
- In case enterprises or consumers first need to reduce a debt burden that has become too high relative to their assets holdings due to fallen asset prices, demand will be pressed down till the debt-asset ratio is back on an acceptable level.
- An external factor as aging demographics may cause a higher savings and lower investment environment.
- External shocks to the economy that increase prices considerably (like increase in oil prices) could lower the demand and put in the economy in recession.
- A growth recession happens when the capacity in the economy expands faster than that demand and the economy grow, resulting in over-capacity and possibly deflation.
- When an economy is facing a period with lesser (growth in) demand due to demographics, nervousness about the future or lack of attractive innovation, and demand cannot be stimulated with lower interest rates, the economy is in a ‘liquidity trap”.
Economic Growth
- Emerging economies that start to export more manufactured goods and services create higher paying jobs; reduce the pressure on land, increase rural wages, lower unemployment, increase wages further and thus increasing their overall prosperity.
- Increasing foreign investment in a country increases the demand for that currency and increases the value of that currency.
- Increasing demand increases import.
- An overheating economy with fast increasing investments, money supply and credits can lead to higher wages and costs, more expensive exports, lower exports, higher imports, and higher currency (trade) deficits.
- Technological development and innovation increase productivity. This drives investment and increases profits, pushing growth, but also limiting inflation.
- An external impulse like increasing exports could get a country out of a slump.
Current Account / Capital Account
- Countries have a current account deficit when they import more than they export.
- If countries are having a current account deficit (imports > exports) it must also have an equal surplus on its capital account (investments from abroad > investments going abroad, including the purchase of foreign equities by the Central Bank).
- When to be concerned in case of a large current account deficit (imports > exports):
- Capital inflows are the result of budget deficits and by government borrowing abroad due to shortage of domestic savings and not by foreign investments.
- Economic growth stays behind on the foreign investments. The reason can be that the currency is too expensive and holding back exports. A devaluation of the currency would be needed.
Read Also Our Other Popular Posts on the Economy
- History of US federal debt as percentage of GDP: Why is This Now Important
- Why is the Japanese Yen so Strong
- Debt or Deficit: are we into trouble compared to other countries?
- Why is China Facing Inflation?
- A 10 year historic overview of the foreign holding of US treasuries
Next & Previous Blog Post
- ‹ previous
- 45 of 174
- next ›